Computer Vision - Experiment 12 - Discrete Fourier Transform Experiment
Experimental objectives and requirements
Understand the basic principle of Fourier transform; master the code writing method to implement Fourier transform.
Experiment content
(i) New project.
(ii) Configure OpenCV in VS2015.
(iii) Read the original image in grayscale mode and display it;
(iv) Write code to implement the Fourier transform;
(v) Display the Fourier transform effect graph.
Experimental apparatus, equipment
A computer with Windows 7 operating system and Visual Studio 2015 installed
Experimental principle
(i) Discrete Fourier transform (DFT), which is the Fourier transform in both the time and frequency domains in a discrete form, transforms the sampling of the time-domain signal into sampling in the frequency domain of the discrete-time Fourier transform. Formally, the sequences at both ends of the transform (in the time and frequency domains) are finite-length, while in practice both sets of sequences should be considered as principal value sequences of discrete periodic signals. Even if a DFT is done for a finite-length discrete signal, it should be transformed again after it has been extended periodically to become a periodic signal. In practical applications, the fast Fourier transform is usually used to compute the DFT efficiently.
(ii) Inside the frequency domain, for an image, places with intense changes in brightness or grayscale correspond to high-frequency components, such as edge and texture information; places with little change in brightness or grayscale correspond to low-frequency components. If the image is subjected to noise that happens to lie within a specific “frequency” range, the original image can be recovered by a filter. Fourier transform can be used in image processing for image enhancement and image denoising, image segmentation and edge detection, image feature extraction, image compression, etc.
Experimental steps
(i) Create Visual Studio 2015 console program;
(ii) Configure OpenCV in Visual Studio 2015;
(iii) Reading the original image in grayscale mode and displaying it;
(iv) Extend the input image to the optimal size, with borders supplemented by 0;
(v) Allocate storage space for the results of the Fourier transform (real and imaginary parts);
(vi) Performing the discrete Fourier transform;
(vii) Convert the complex numbers into magnitudes;
(viii) Performing logarithmic scale scaling;
(ix) shear and redistribute the magnitude map quadrant;
(x) Normalization, transforming the matrix into a visual image format using floating point values between 0 and 1;
(xi) Display the Fourier transform effect map.
Experimental notes
(i) The method of configuring OpenCV in VS after completing the installation of OpenCV;
(ii) The functions and usage of the dft function;
(iii) The method of clipping and redistributing magnitude map quadrants;
(iv) The function and usage of the normalize function.
Experimental results
(i) Experimental code
|
|
(ii) Show results

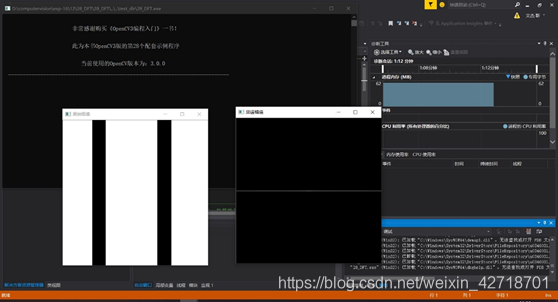
Experiment summary
The main content of this experiment is to understand the basic principle of Fourier transform; to master the code writing method to implement Fourier transform. Create a new project, configure OpenCV in VS2015; read the original image in grayscale mode and display it; write code to realize the Fourier transform; display the Fourier transform effect graph.