Computer Vision - Experiment 14 - Watershed algorithm experiment
Experimental objectives and requirements
Understand the basic principles of the watershed algorithm; master the code writing method to implement the watershed algorithm.
Experiment content
(i) New project .
(ii) Configuring OpenCV in VS2015.
(iii) Load the original image and display it, initialize the mask and grayscale map;
(iv) Finding the contours;
(v) Copy the mask.
(vi) loop to draw out the contours;
(vii) traversing the watershed image to save it;
(viii) Mix the grayscale and watershed effect maps and display the final window.
Experimental apparatus, equipment
A computer with Windows 7 operating system and Visual Studio 2015 installed.
Experimental principle
(i) In many practical applications, we need to segment the loft image, but cannot get useful information from the background image. Watershed algorithm is often very effective in this regard. This algorithm can transform the edges of the image into “mountains” and uniform areas into “valleys” so as to help segment the target. Watershed algorithm is a mathematical morphological segmentation method based on topological theory. The basic idea is to consider the image as a topological landscape in geodesic terms, and the gray value of each pixel in the image represents the elevation of the point. The concept and formation of the watershed can be illustrated by simulating the immersion process: on the surface of each local minima, a small hole is pierced, and then the whole model is slowly immersed in water. As the immersion deepens, the influence domain of each local minima slowly expands outward, and a dam is constructed at the confluence of the two catchment basins, i.e., the watershed is formed.
(ii) The watershed algorithm implemented by the function watershed is one of the marker-based segmentation algorithms. Before passing the image to the function, we need to roughly outline the regions of the image that are expected to be segmented, and they are labeled as positive indices. So, each region is labeled with pixel values 1, 2, 3, etc., indicating that it becomes one or more connected components. The values of these markers can be retrieved by a binary mask using the findContours function and the drawContours function.
Experimental steps
(i) Create the Visual Studio 2015 console application;
(ii) Configure OpenCV in Visual Studio 2015;
(iii) Calling the imread function to load the original image and display it, initializing the mask and grayscale map;
(iv) Calling the findContours function to find contours;
(v) Copy the mask.
(vi) call the drawContours function to loop through the contours;
(vii) Call the watershed function to calculate the watershed, using a double-layer loop to traverse the watershed image and save it;
(viii) Blend the grayscale and watershed effect maps and display the final window.
Experimental notes
(i) The method of configuring OpenCV in VS after completing the installation of OpenCV;
(ii) The functions and usage of the watershed function;
(iii) The method of traversing the saved watershed images;
(iv) The method of mixing grayscale and watershed effect maps.
Experimental results
(i) Experimental code
|
|
(ii) Show results
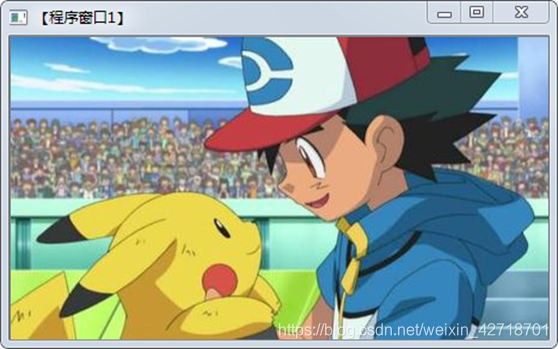
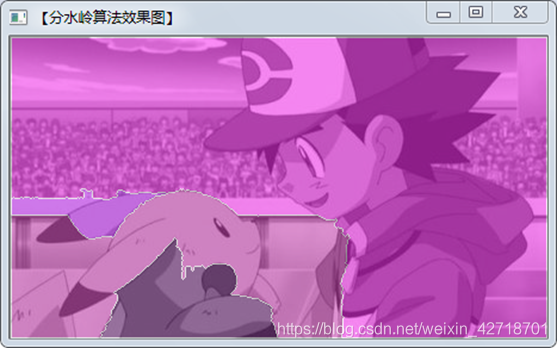
Experiment Summary
The main content of this experiment is to understand the basic principle of the watershed algorithm; to master the code writing method to implement the watershed algorithm. Create a new project, configure OpenCV in VS2015, load the original image and display it, initialize the mask and grayscale map, find the contours, copy the mask, loop through the contours, save the watershed image traversal, mix the grayscale and watershed effect maps and display the final window.