Computer Vision - Experiment 16 - Separate background experiments with Gaussian background modeling
Experimental objectives and requirements
Understand the basic principles of background modeling; master the code writing method to implement background modeling.
Experiment content
(i) Create a new project.
(ii) Configure OpenCV in VS2015.
(iii) Opening a video using the VideoCapture class;
(iv) Creating a Gaussian blend model;
(v) Update the Gaussian blending model by updating each image frame of the opened video.
(vi) Show the foreground image and the background image.
Experimental apparatus, equipment
A computer with Windows 7 operating system and Visual Studio 2015 installed.
Experimental principle
(i) In many cases, we need to find the target of interest from a video or a series of images, for example, to sound an alarm when a person enters a supermarket that is already closed. To do this, we first need to “learn” the background model, and then compare the background model with the current image to get the foreground target.
(ii) background and foreground are relative concepts, take the highway as an example: sometimes we are interested in the cars coming and going on the highway, then the cars are the foreground, while the road and the surrounding environment are the background; sometimes we are only interested in the pedestrians breaking into the highway, then the intruders are the foreground, while other things, including cars, become the background. All kinds of background models have their own application occasions.
(iii) Mixture of Gaussians (MOG) is an advanced background statistical model implemented by OpenCv. Gaussian model is to quantify things precisely with Gaussian probability density function (normal distribution curve), and decompose one thing into several models formed based on Gaussian probability density function (normal distribution curve). The principle and process of building a Gaussian model for an image background:The image gray histogram reflects the frequency of occurrence of a certain gray value in an image, which can also be thought of as an estimate of the image gray probability density. If the target area and the background area contained in the image are relatively different, and the background area and the target area have a certain difference in gray level, then the gray level histogram of the image shows a double peak-valley shape, where one peak corresponds to the target and the other peak corresponds to the central gray level of the background. For complex images, especially medical images, they are usually multi-peaked. By considering the multi-peak property of the histogram as a superposition of multiple Gaussian distributions, the image segmentation problem can be solved.
Experimental steps
(i) Create a Visual Studio 2015 console program;
(ii) Configure OpenCV in Visual Studio 2015;
(iii) Call the open function of VideoCapture to open the video;
(iv) Calling the BackgroundSubtractorMOG2 class to create a Gaussian mixture model;
(v) Call the “»” method of the VideoCapture class to read a frame of the video;
(vi) Update the Gaussian blending model by updating each frame of the opened video and calling the getBackgroundImage function to get the background image.
(vii) Call the imshow function to display the foreground image and the background image.
Experimental notes
(i) The method of configuring OpenCV in VS after completing the installation of OpenCV;
(ii) The functions and usage of the VideoCapture class;
(iii) The functions and usage of the BackgroundSubtractorMOG2 class;
(iv) The functions and usage of getBackgroundImage function.
Experimental results
(i) Experimental code
|
|
(ii) Show results



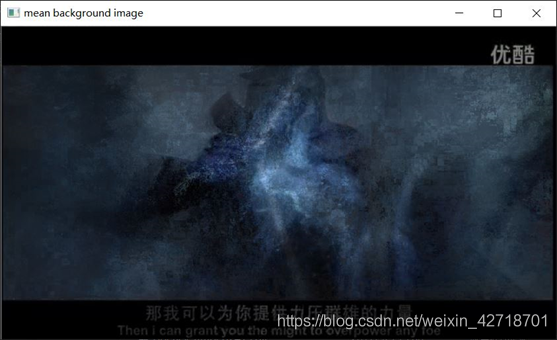
Experiment summary
The main content of this experiment is to understand the basic principles of background modeling; master the code writing method to implement background modeling. Create a new project; configure OpenCV in VS2015; open a video using the VideoCapture class; create a Gaussian blending model; update the Gaussian blending model by updating each frame of the opened video; display the foreground image and the background image.