Computer Vision - Experiment 6 - Haff transform experiment
Experimental objectives and requirements
Understand the basic principle of Haff transform; master the code writing method to implement Haff transform using OpenCV.
Experiment content
(i) Create a new project.
(ii) Configuring OpenCV in VS2015.
(iii) Implement the Haff transform to detect line segments using the functions in OpenCV.
Experimental instruments, equipment
A computer with Windows 7 operating system and Visual Studio 2015 installed
Experimental principle
(i) In the field of image processing and computer vision, how to extract the required feature information from the current image is the key to image recognition. In many applications fieldsh need to detect straight lines or circles quickly and accurately, one of the very effective ways to solve the problem is the Haff transform.
(ii) Haff line transform is a method used to find straight lines. Before using Haff line transform, the image is first processed for edge detection, i.e., the direct input of Haff line transform can only be edge binary image.
(iii) In OpenCV, the HoughLines function can be used to call the standard Haff transform and the multiscale Haff transform. And the HoughLinesP function is used to invoke the cumulative probability Hough transform. The cumulative probability Hough transform is executed very efficiently, and we prefer to use the HoughLinesP function compared to the HoughLines function.
Experimental steps
(i) Create the Visual Studio 2015 console program;
(ii) Configure OpenCV in Visual Studio 2015;
(iii) Write code to implement the Haff line transform to detect line segments using the HoughLines or HoughLinesP function.
Experimental notes
(i) Configure OpenCV in VS after completing the installation of OpenCV;
(ii) The functions and usage of HoughLines or HoughLinesP functions.
Experimental results
(i) Experimental code
|
|
(ii) Show results

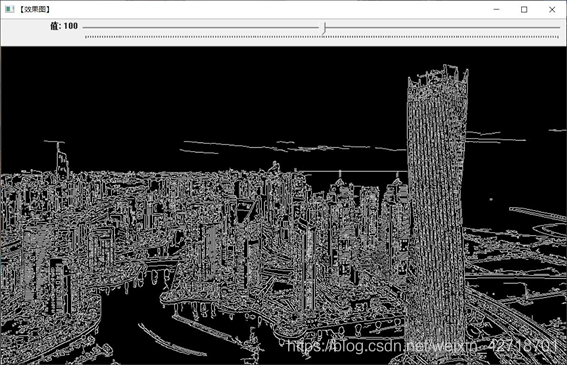
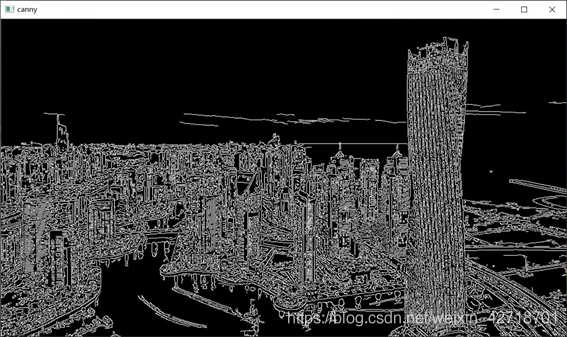
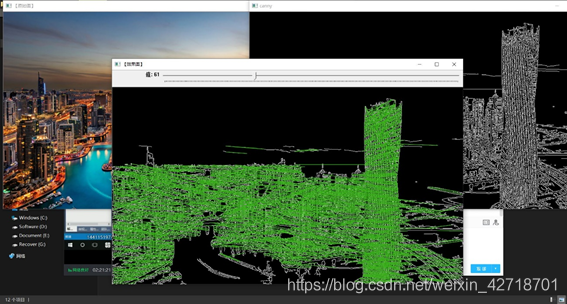
Experiment Summary
The main content of this experiment is to understand the basic principle of Haff transform; master the code writing method to implement Haff transform using OpenCV. Create a new project, configure OpenCV in VS2015, and use the functions in OpenCV to implement the Haff transform to detect line segments. Use the HoughLines function to call the standard Haff transform and the multi-scale Haff transform, and the HoughLinesP function to call the cumulative probability Haff transform. By writing code, I learned to use the HoughLines function to call the standard Haff transform and the multiscale Haff transform, and the HoughLinesP function to call the cumulative probability Hough transform.