Simple Factory Pattern and Factory Method Pattern
Simple Factory Pattern
Simple Factory Pattern Concept
The Simple Factory Pattern is not one of GoF’s 23 classic design patterns, but it is often used as a basis for learning other factory patterns.
Simple Factory Pattern: Define a factory class that can return instances of different classes depending on the parameters, and the instances that are created usually have a common parent class.
Simple Factory Pattern Structure
Simple Factory Pattern Structure: The structure of the Simple Factory Pattern is relatively simple, and its core is the design of the factory class.
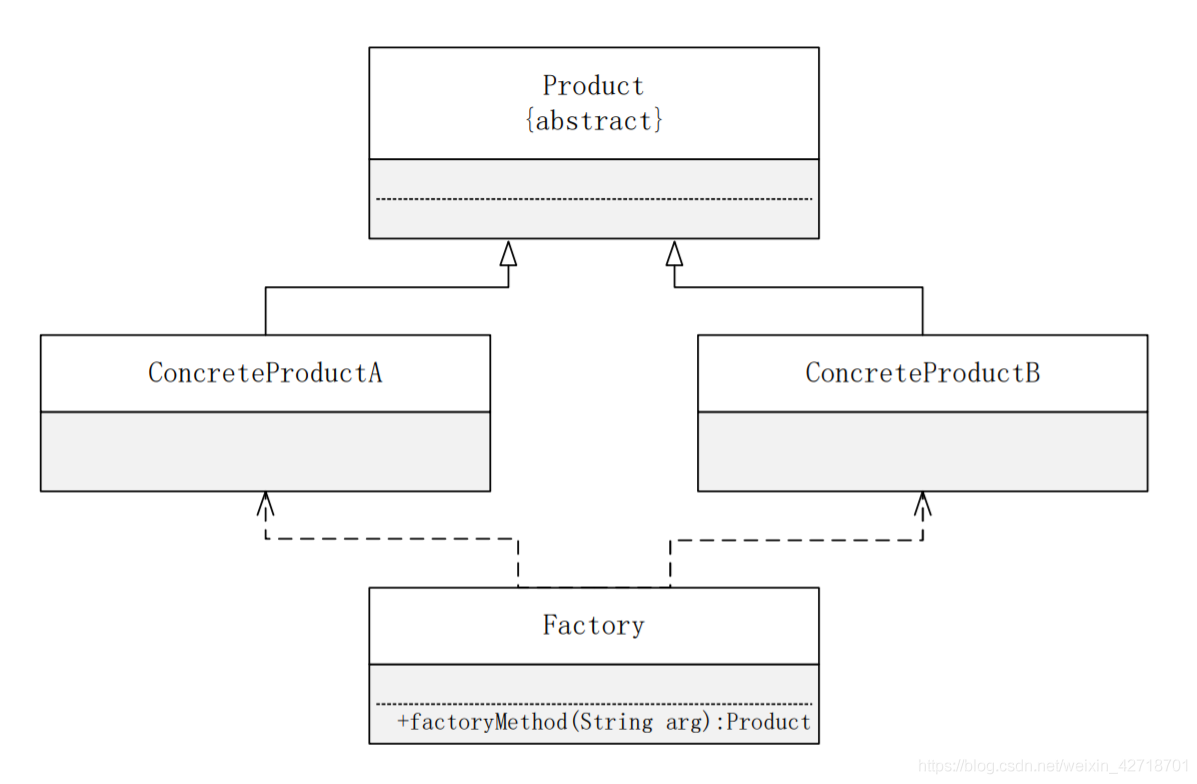
(1) Factory (factory role): The factory role is the factory class, which is the core of the simple factory pattern and is responsible for implementing the internal logic of creating all product instances; the factory class can be called directly by the outside world to create the required product objects; static factory methods are provided in the factory class factoryMethod(), which returns a type of abstract product type Product.
(2) Product (abstract product role): It is the parent of all objects created by the factory class, encapsulating the public methods of various product objects, its introduction will improve the flexibility of the system, making it possible to define only a generic factory method in the factory class, because all the concrete product objects created are its sub class objects.
(3) ConcreteProduct (Concrete Product Role): It is the creation goal of the Simple Factory pattern, and all created objects act as instances of some concrete class of this role. Each concrete product role inherits from the abstract product role and needs to implement the abstract methods declared in the abstract product.
Simple Factory Pattern Implementation
A typical abstract product class code is as follows:
|
|
The code for a typical specific product class is as follows:
|
|
The code of a typical factory class is as follows:
|
|
In the client code, the product object is obtained by calling the factory method of the factory class. The typical code is as follows:
|
|
Simple factory pattern advantages and disadvantages and applicable environment
Simple Factory Pattern Advantages
(1) The factory class contains the necessary judgment logic to decide when to create an instance of which product class, the client can dispense with the responsibility of creating the product object directly, but only “consume” the product, the simple factory pattern achieves the separation of object creation and use. The simple factory pattern achieves the separation of object creation and use.
(2) The client does not need to know the class name of the specific product class created, only the parameters corresponding to the specific product class can be, for some complex class names, through the simple factory pattern can reduce the amount of user memory to a certain extent.
(3) By introducing configuration files, new concrete product classes can be replaced and added without modifying any client code, which improves the flexibility of the system to a certain extent.
Simple Factory Pattern Disadvantages
(1) Because the factory class concentrates all the product creation logic, the responsibilities are too heavy and once it does not work properly, the whole system has to be affected.
(2) Using the simple factory pattern will inevitably increase the number of classes in the system (introducing new factory classes), increasing the degree of responsibility and understanding of the system.
(3) The system is difficult to extend, once you add a new product you have to modify the factory logic, which may cause the factory logic to be too complex when there are more product types, which is not conducive to system expansion and maintenance.
(4) The simple factory pattern, due to the use of static factory methods, causes the factory role to fail to form an inheritance-based hierarchy.
Simple Factory Pattern Applicable Environment
(1) The factory class is responsible for creating fewer objects, due to the creation of fewer objects, due to the creation of fewer objects, does not cause the business logic in the factory methods to be too complex.
(2) The client only knows the parameters passed into the factory class and does not care about how the object is created.
Factory Method Pattern
Factory method pattern concept
In the factory method pattern no longer provides a unified factory class to create all product objects, but rather provides different factories for different products, and the system provides a factory hierarchy that corresponds to the product hierarchy.
The Factory Method Pattern: Define an interface for creating objects, but let subclasses decide which class to instantiate. The factory method pattern lets the instantiation of a class be deferred to its subclasses.
Factory Method Pattern Structure
Factory Method Pattern Structure: The Factory Method Pattern provides an abstract factory interface to declare abstract factory methods, and its subclasses to concretely implement the factory methods to create concrete product objects.
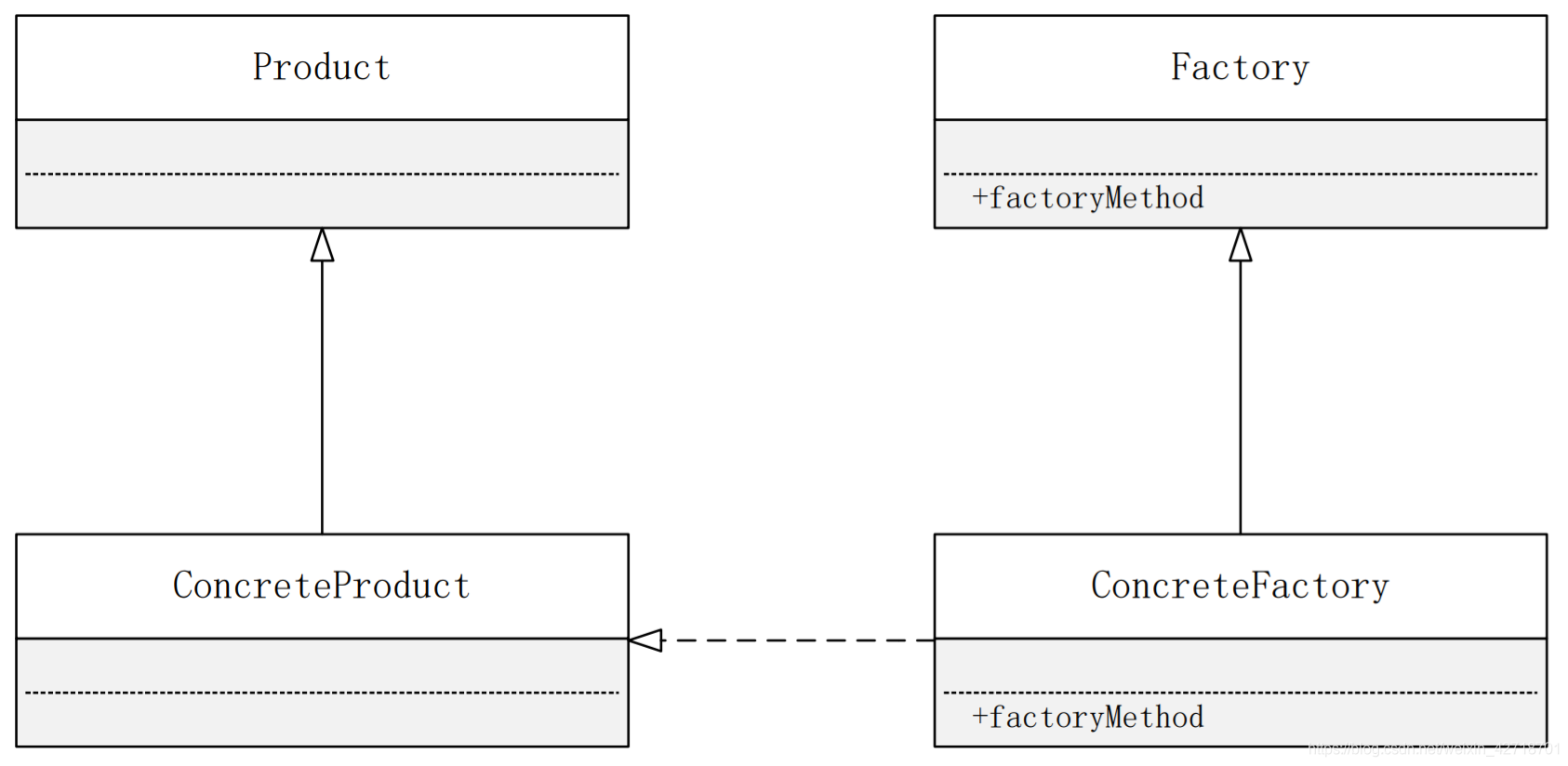
(1) Product (abstract product): It is the interface that defines the product, the supertype of the object created by the factory method pattern, which is the public parent class of the product object.
(2) ConcreteProduct (Concrete Product): It implements the abstract product interface, some type of concrete product created by a specialized concrete factory, one-to-one correspondence between the concrete factory and the concrete product.
(3) Factory (abstract factory): A factory method (Factory Method) is declared in the abstract factory class for returning a product. The abstract factory is the core of the factory method pattern, and all factory classes that create objects must implement the interface.
(4) ConcreteFactory (Concrete Factory): It is a subclass of the abstract factory class that implements the Factory Method declared in the abstract factory and can be called by the client to return an instance of the concrete product class.
Factory method pattern implementation
Compared with the simple factory pattern, the most important feature of the factory method pattern is the introduction of the abstract factory role, which can be an interface, an abstract class or a concrete class. Its typical code is as follows:
|
|
In the abstract factory declared factory methods but does not implement the factory methods, the creation of concrete product objects by its subclasses responsible for the client for the abstract factory programming, you can specify the concrete factory class at runtime, the concrete factory class implements the factory methods, different concrete factory can create different concrete products. Its typical code is as follows:
|
|
In practice, the specific factory class can be responsible for the initialization of the product object and some resource and environment configuration work, such as connecting to the database and creating files, in addition to creating specific product objects when the factory method is implemented.
In the client code, the developer only needs to care about the factory class, and different concrete factories can create different products. A typical client-side code snippet is as follows:
|
|
You can store the class name of the concrete factory class ConcreteFactory through the configuration file, and then create the concrete factory object through the reflection mechanism, without modifying the source code when replacing the new concrete factory, and the system is more convenient to extend.
Factory method pattern advantages and disadvantages and applicable environment
Advantages of the Factory Method Pattern
(1) In the factory method pattern, the factory method is used to create the product that the customer needs, while also hiding from the customer which specific product class will be instantiated this detail, the user only needs to care about the factory corresponding to the desired product, without caring about the creation details, or even without knowing the class name of the specific product class.
(2) The polymorphic design based on the factory role and product role is the key to the factory method pattern. It enables the factory to determine autonomously what product object to create, and the details of how to create this object are completely encapsulated within the concrete factory. The factory method pattern is also known as the polymorphic factory pattern precisely because all concrete factory classes have the same abstract parent class.
(3) Another priority of using the factory method pattern is to add new products to the system without modifying the interface provided by the abstract factory and abstract product, without modifying the client, and without modifying other concrete factories and concrete products, but just add a concrete factory and concrete products, so that the scalability of the system also becomes The scalability of the system becomes very good, fully consistent with the principle of open and closed.
Drawbacks of the Factory Method Pattern
(1) When adding new products, you need to write a new specific product class, and also provide the corresponding specific factory class, the number of classes in the system will increase in pairs, to a certain extent, increasing the complexity of the system, there are more classes to compile and run, which will bring some additional overhead to the system.
(2) As the scalability of the system is taken into account, the abstraction layer needs to be introduced, which is defined in the client code using the abstraction layer, increasing the abstraction and understanding difficulty of the system.
Factory Method Pattern Applicable Environment
(1) The client does not know the class of the object it needs. In the factory method pattern, the client does not need to know the class name of the specific product class, it only needs to know the corresponding factory. The specific product object is created by the specific factory class, and the class name of the specific factory class can be stored in the configuration file or database.
(2) abstract factory class through its subclasses to specify the creation of that object. In the factory method pattern, for the abstract factory class only need to provide an interface to create the product, and by its subclasses to determine the specific object to be created, the use of object-oriented polymorphism and the principle of Richter substitution, in the program runtime child class objects will override the parent class objects, thus making the system more easily scalable.
Difference between “Simple Factory Pattern” and “Factory Method Pattern
(1) The simple factory pattern is difficult when you need to add new product classes, you need to change the original code, not in line with the open and closed principle; and the factory method pattern does not need to change the original code when you add new product classes, fully in line with the open and closed principle.
(2) The factory method pattern is more complex, more abstract, more system resource intensive, and more difficult to understand than the simple factory pattern.
(3) The simple factory pattern in the factory class concentrates all the product creation logic, once it does not work properly, the whole system will be affected; while the factory method pattern divides the responsibility to each factory class, reducing the responsibility of each class.